Maintaining temperature within a predefined range is crucial to ensure the proper functioning and longevity of a hydraulic system, particularly the seals. In a hydraulic circuit, the thermal regulation of the working fluid, usually hydraulic oil, is essential for efficient energy transmission and for preventing damage due to excessive heating or cooling.
Operation of a Hydraulic Circuit
A hydraulic circuit is a closed system where hydraulic oil flows through various components that work together to transmit energy. The main components of a hydraulic circuit include:
- Pump: Generates the flow of oil within the circuit.
- Valves: Regulate the pressure, flow, and direction of the fluid.
- Actuators: Such as hydraulic cylinders and motors, convert the fluid’s energy into mechanical work.
- Filter: Removes impurities from the fluid to prevent damage to components.
- Reservoir: Contains the hydraulic oil and allows for heat dissipation.
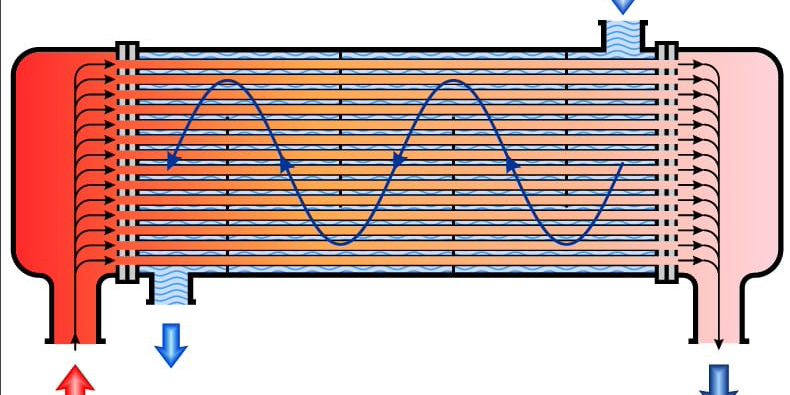
- Heat Exchanger: Regulates the oil temperature to keep it within safe operational limits.
Importance of Thermal Regulation
The fluid temperature in a hydraulic circuit increases during operation due to friction losses in the conduits and inefficiencies in energy transformations. If the temperature exceeds permissible limits, it can compromise the fluid’s characteristics and damage the system and seals. Therefore, it is essential to maintain the hydraulic oil at the temperature specified by the designer. Thermal regulation, achieved through heat exchangers, is vital to ensure that the fluid operates under optimal conditions.
Types of Heat Exchangers
Heat exchangers are devices that allow heat transfer between fluids at different temperatures. They are primarily classified into two categories:
- Air-Oil Exchangers: Use air to cool the oil. They are often installed on the return lines of hydraulic circuits and constructed with aluminum radiant masses to enhance thermal efficiency and pressure resistance.
- Water-Oil Exchangers: Use water to cool the oil. They are made with small diameter copper tubes and are suitable for cooling hydraulic systems, plastic and rubber injection molding presses, and machine tools.
Maintenance of Heat Exchangers
Preventive and regular maintenance of heat exchangers is crucial to maintain their efficiency and extend their operational life. Maintenance operations include cleaning the heat exchange surfaces from impurities such as grease, dust, and leaves, which can reduce radiator efficiency and lead to system overheating. Cleaning can be performed with descaling solutions and, in the case of scale build-up, mechanically.
Industrial Applications of Heat Exchangers
Heat exchangers find applications in numerous industrial sectors, including:
- Construction Sector: Construction machines like mobile cranes, truck-mounted cranes, concrete mixers, and concrete pumps use hydraulic systems for moving parts. Temperature regulation of the oil is crucial for their operation.
- Agricultural Sector: Soil processing, seeding, and transplanting machines require hydraulic systems with advanced electronics and digital controls, where thermal regulation is essential.
- Earth Moving Machines: Excavators, bulldozers, and drills use complex hydraulic systems that need effective oil thermal regulation.
- Machine Tools: Include all machines that transform material by deformation or chip removal, such as lathes, grinders, and hydraulic presses. The quality and constant temperature of hydraulic fluid are essential.
- Steel and Metallurgy: Hydraulic applications are numerous, especially in casting plants and metal rolling.
Conclusion
Heat exchangers, although well-established components, remain critical elements in hydraulic systems. The various construction solutions provided by the industry allow maximum design freedom, meeting diverse operational needs. Their careful design and regular maintenance are essential to ensure the efficient and reliable operation of hydraulic systems in a wide range of industrial applications.
Stefano Serri